Recovery¶
On this page, we will explain the three possible scenarios regarding recoveries, from the "most" probable to the "least". In all three cases, we will use the DLM backup policies defined on the backup page.
Shared resources¶
In this section, I will simulate that a user has deleted an important file named Nomimas 2023.pdf in a shared resource called rrhh. The general process will be as follows:
- We will check the existence of the resource and then delete it.
- We will create an EBS volume from the latest available snapshot.
- We will mount the volume in a temporary location.
- We will restore the deleted file.
- We will verify that the user has the file again and that it is accessible.
- We will unmount and delete the volume.
To simulate the loss of the important document, I will simply connect with the user, check the existence of the document, and delete it.
-
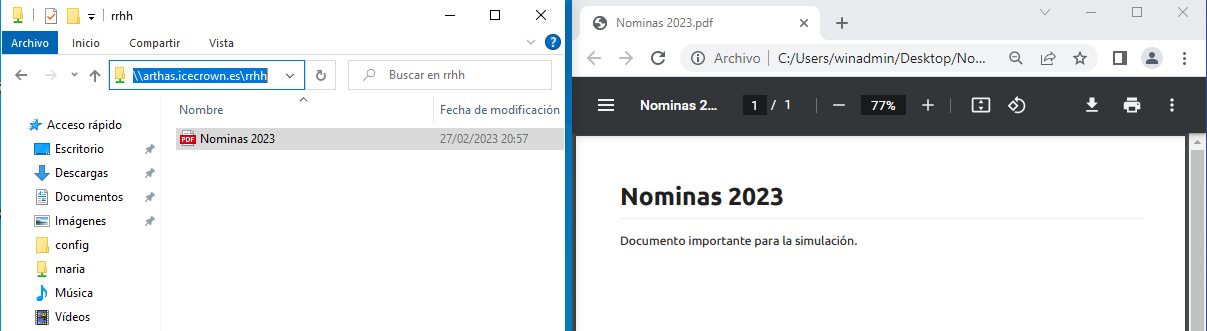
With the user, we will check the existence of the document in the shared resource:
-
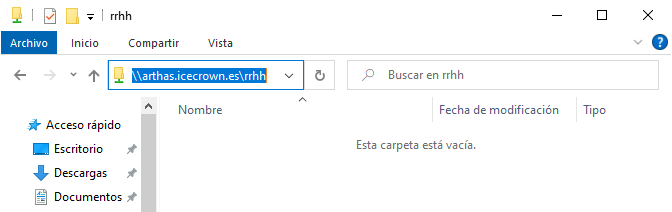
We will delete the resource:
With the simulated disaster, we will proceed with its recovery.
-
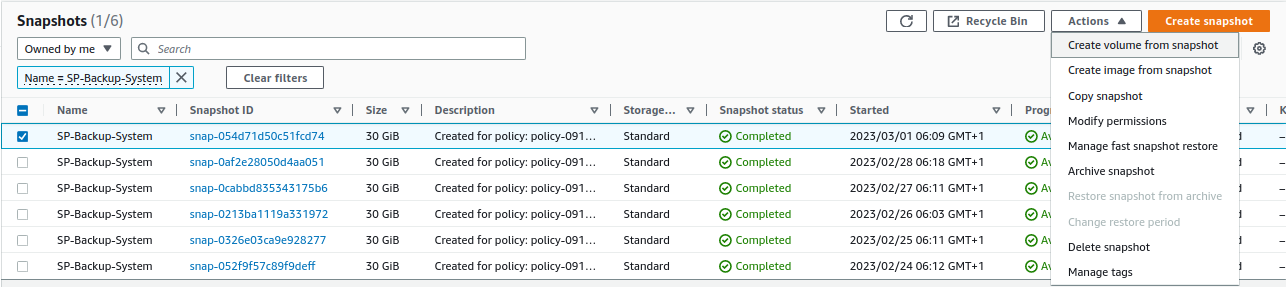
From
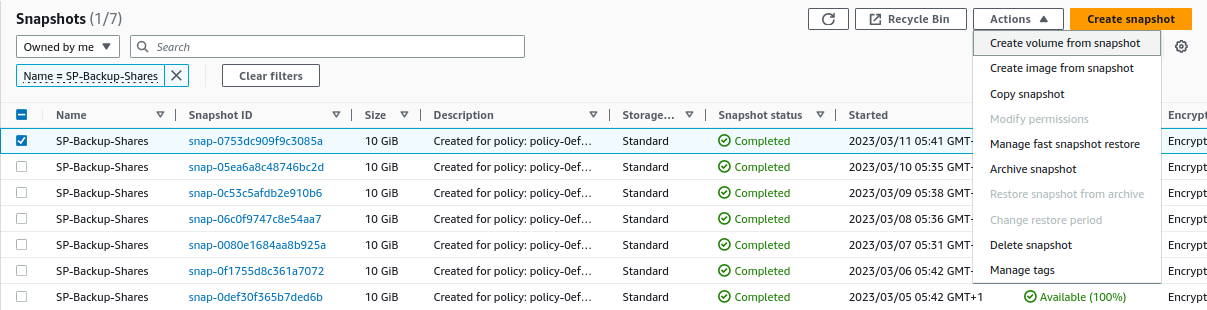
EC2 -> Elastic Block Store -> Snapshots -> Create volume from snapshot, we select the latest snapshot and create a volume: -
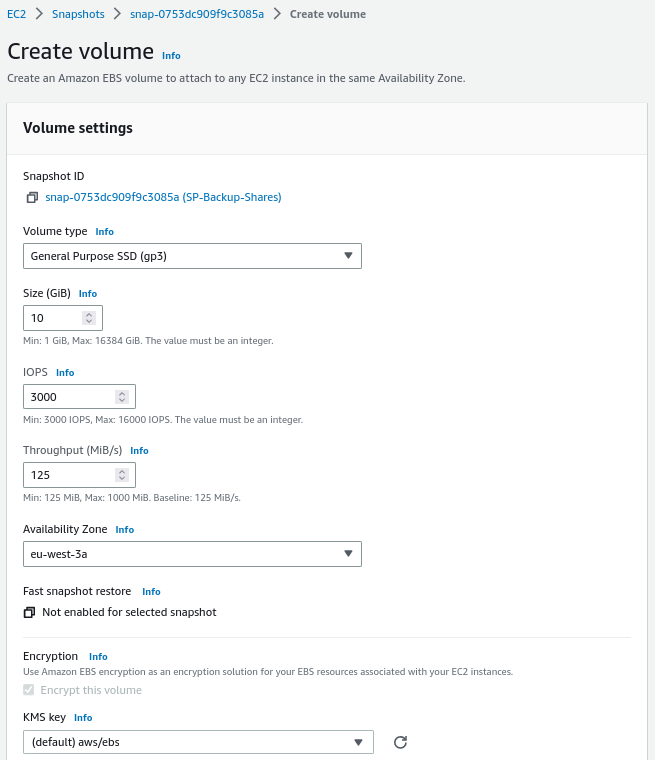
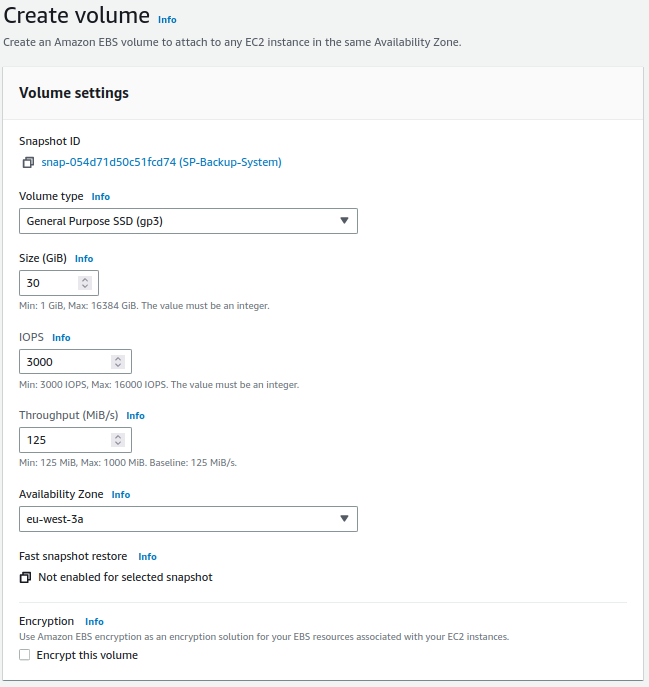
We configure the temporary volume:
Warning
It must be created in the same availability zone.
-
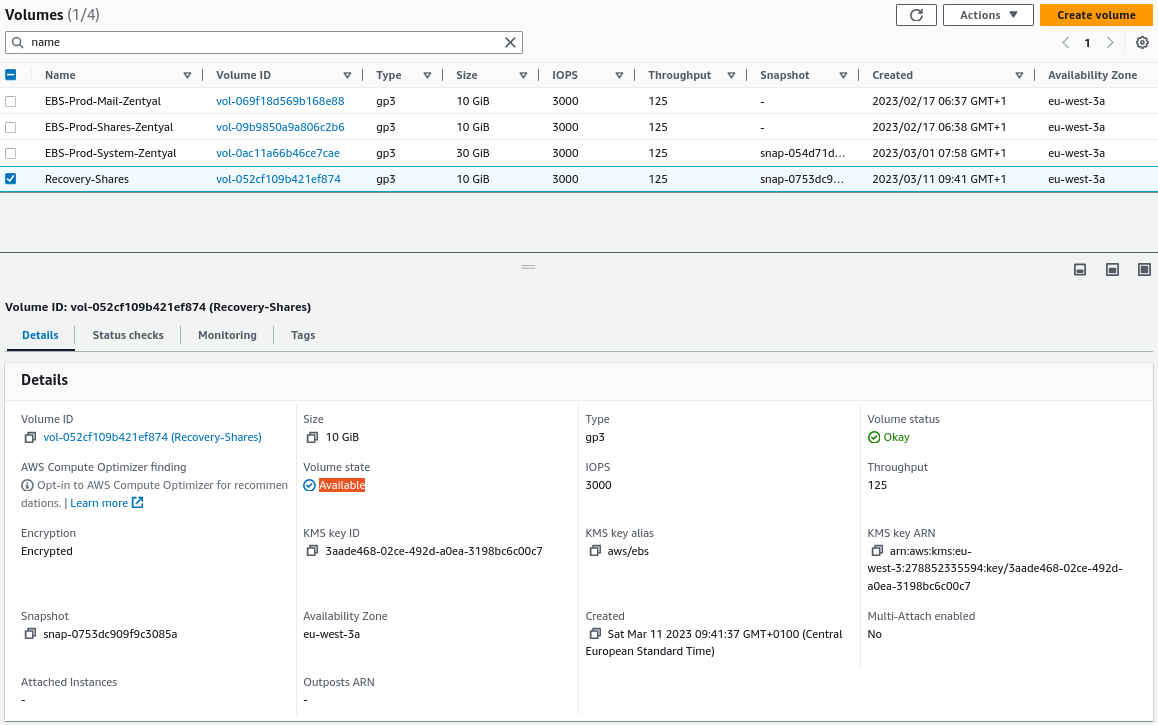
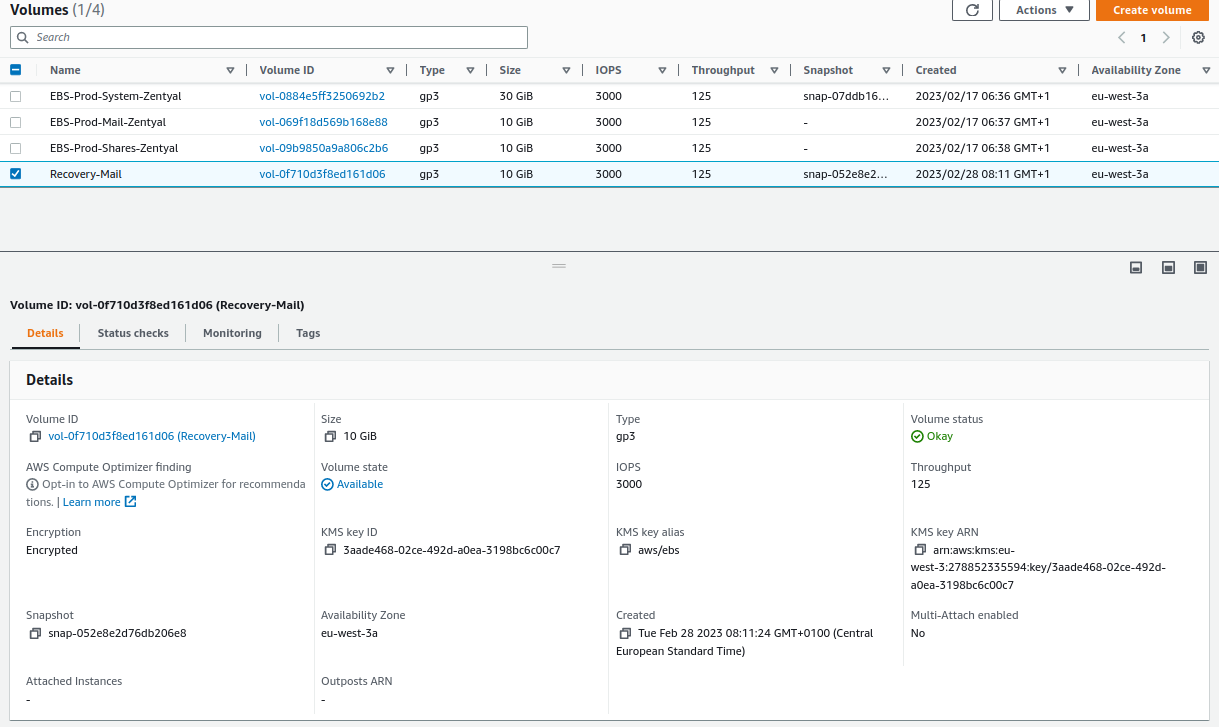
We verify that the volume has been successfully created and is available:
-
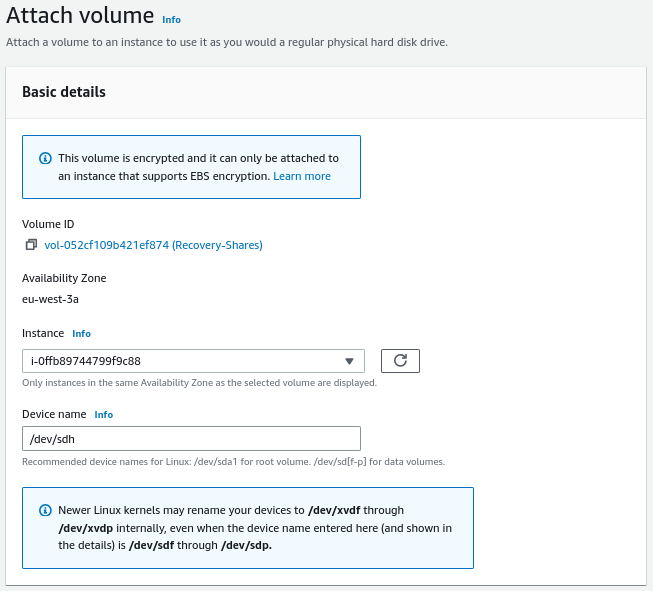
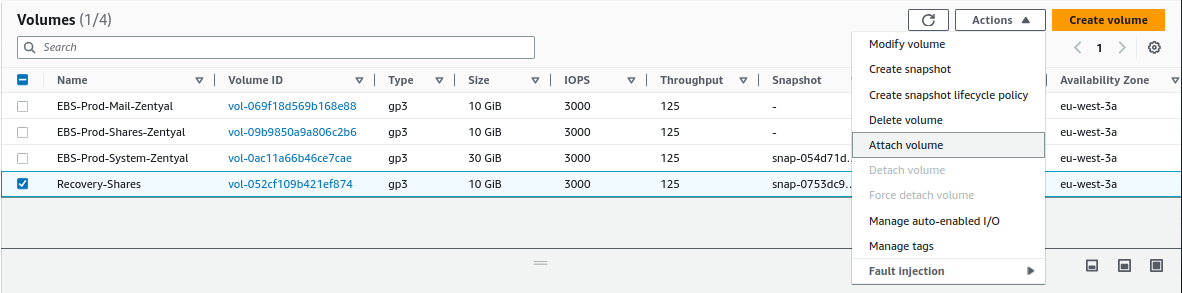
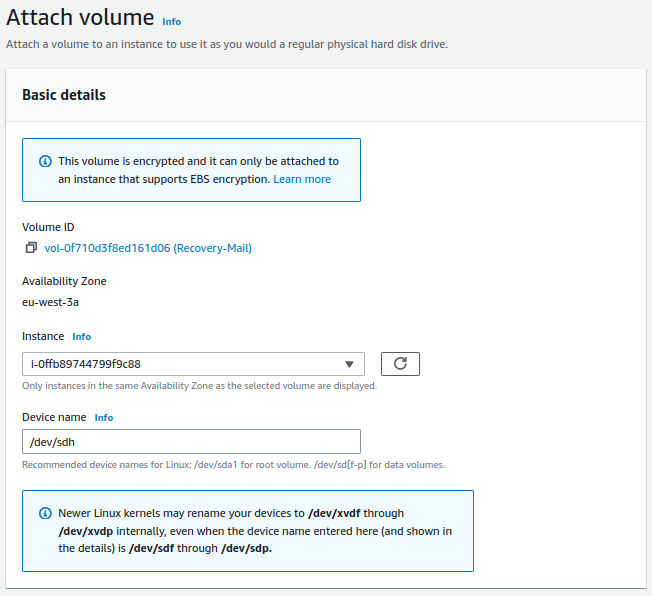
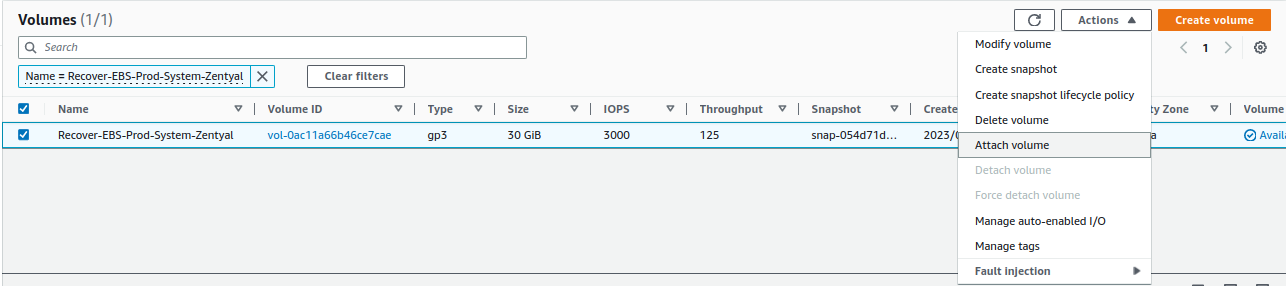
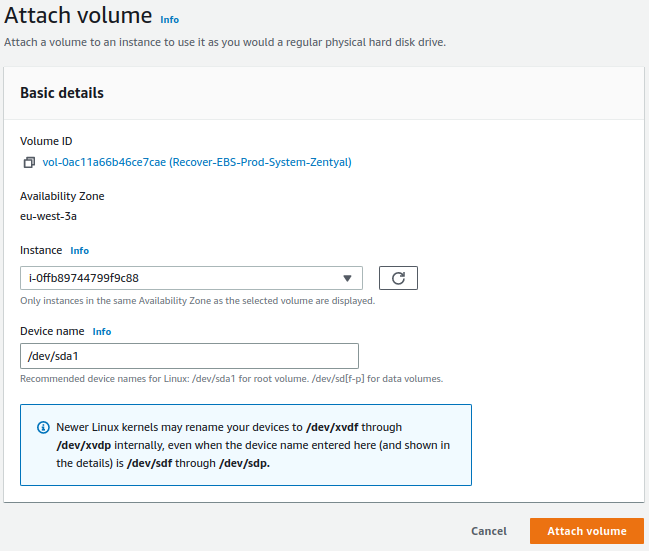
We attach the volume to the instance, for that, we go to
Actions -> Attach volume: -
We connect via SSH to the server and verify that the operating system detects the new volume:
In my environment, the volume has been mounted as
nvme3n1p1: -
We create a temporary directory where we will mount the new disk:
-
We mount the volume:
-
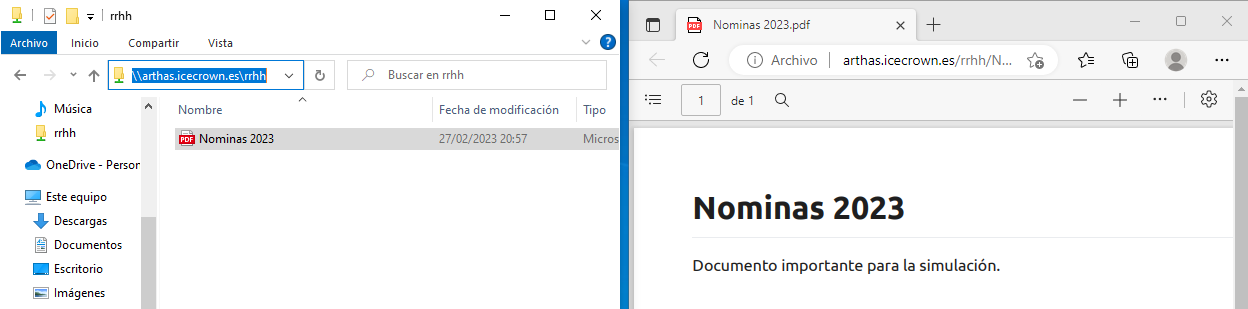
We search for the document in the shared resource
rrhhin the directory where we mounted the temporary disk:Example on my server:
-
Once the file has been identified, we proceed with its restoration:
Warning
It is important to use the
-poption to preserve the file permissions, otherwise, the user won't be able to access it. -
From the user, we verify that the file was recovered and that it is accessible:
-
Once we have confirmed the restoration of the file, we proceed to unmount the disk and delete the temporary directory created:
-
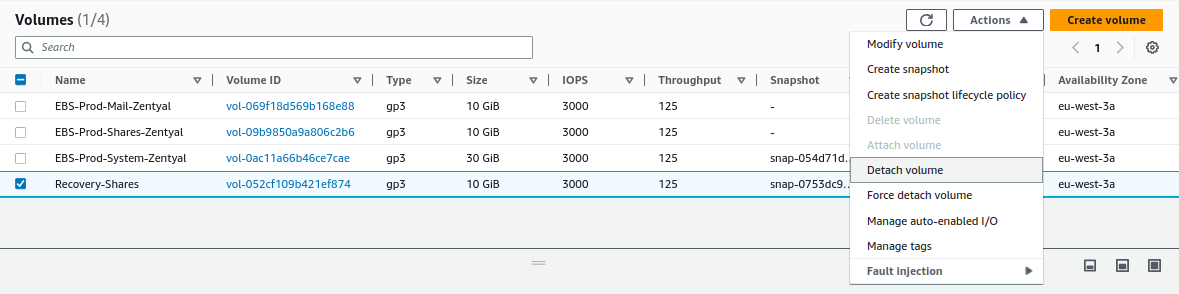
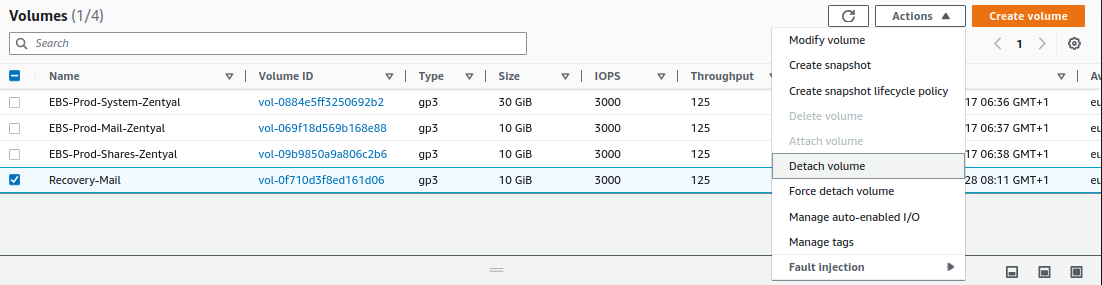
We detach the EBS volume from the instance, for that, we go to
Actions -> Detach volume: -
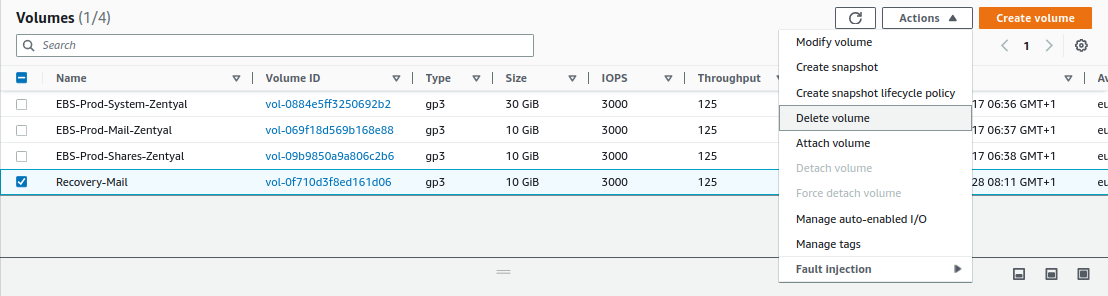
Finally, we delete the EBS volume from
Actions -> Delete volume:
Emails¶
The objective of this section is to simulate that a user named maria has deleted an email called Presupuesto 2023 with an attachment. The general process is very similar to the previous one, which consists of:
- We will check the existence of the email and then delete it.
- We will create an EBS volume from the latest available snapshot.
- We will mount the volume in a temporary location.
- We will restore the deleted email.
- We will check that the user has access to the email again.
- We will unmount and delete the volume.
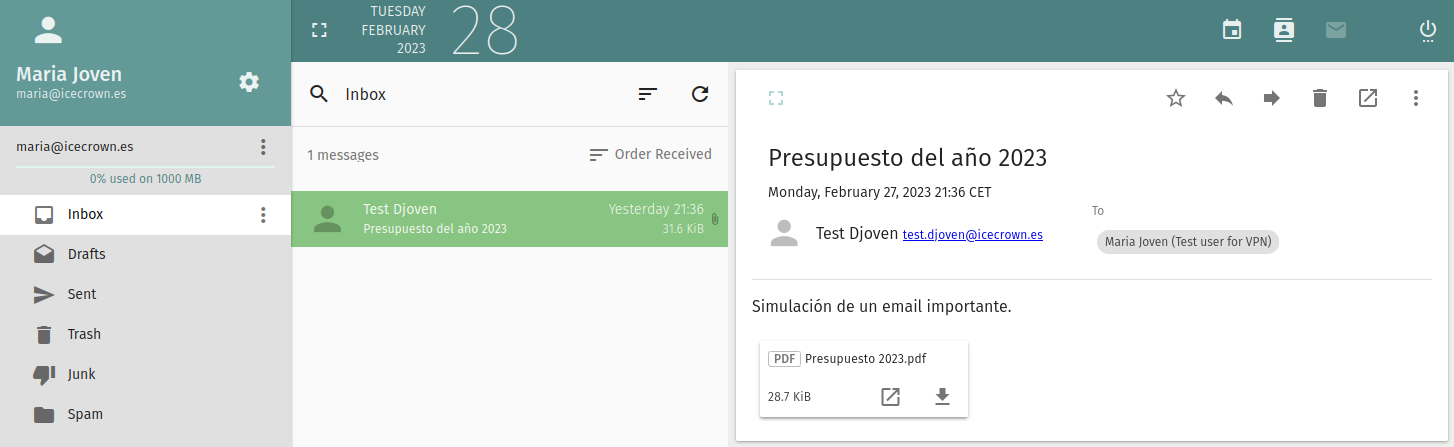
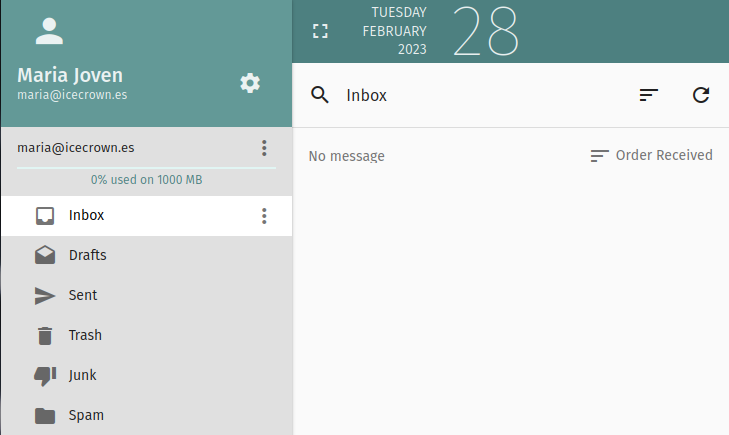
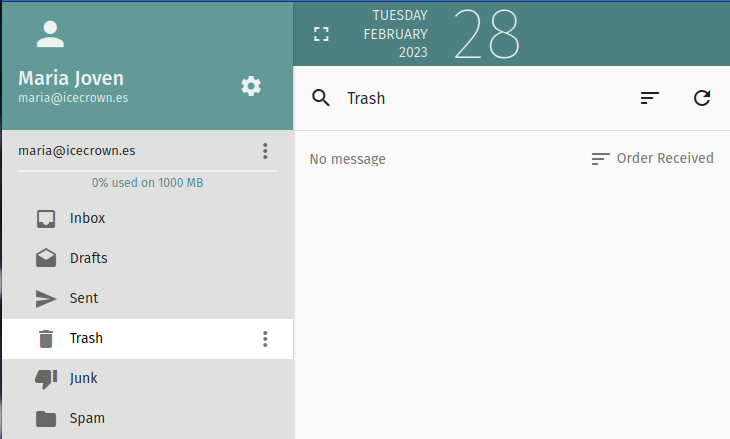
To simulate the loss of an important email, I will use the webmail to check the email and then delete it.
Now that we have simulated the disaster, we will proceed to perform the necessary actions to recover the email.
-
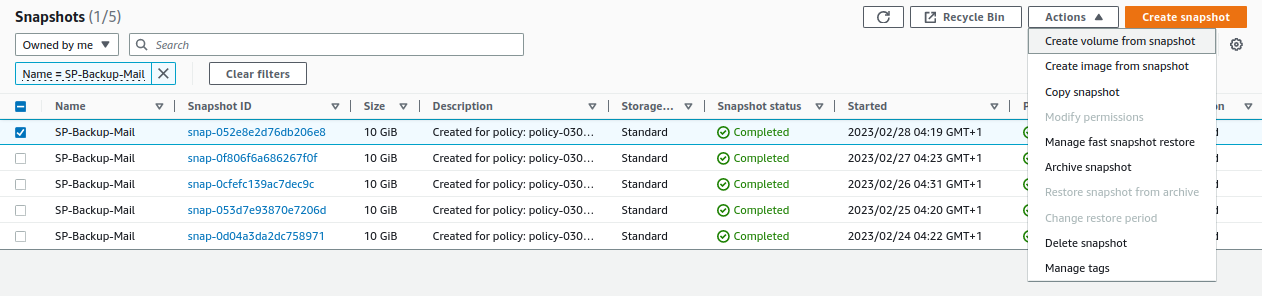
From
EC2 -> Elastic Block Store -> Snapshots -> Create volume from snapshotwe select the latest snapshot and create a volume: -
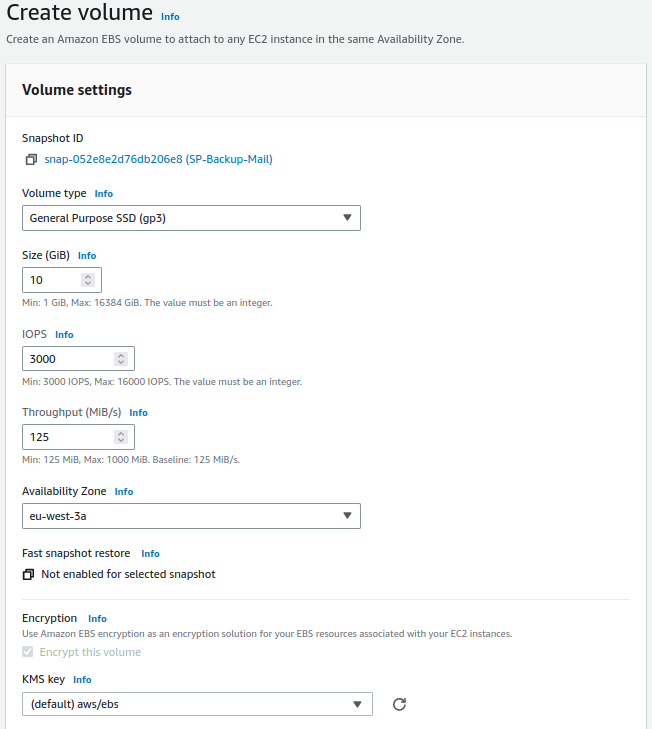
We configure the temporary volume:
Warning
It must be created in the same availability zone.
-
We verify that the volume has been created successfully and is available:
-
We attach the volume to the instance, for this, we go to
Actions -> Attach volume: -
We connect via SSH to the server and check that the operating system detects the new volume:
In my environment, the volume has been mounted as
nvme3n1p1: -
We create a temporary directory where we will mount the new disk:
-
We mount the volume:
-
We search for the email of the user
mariain the directory where we have mounted the temporary disk:Example on my server:
-
Once the email has been identified, we proceed to restore it:
Warning
It is important to use the
-poption to preserve the file permissions, otherwise, the user will not be able to access it. Additionally, it will also be important to restore it in the same directory, which in my case is:icecrown.es/maria/Maildir/cur/. -
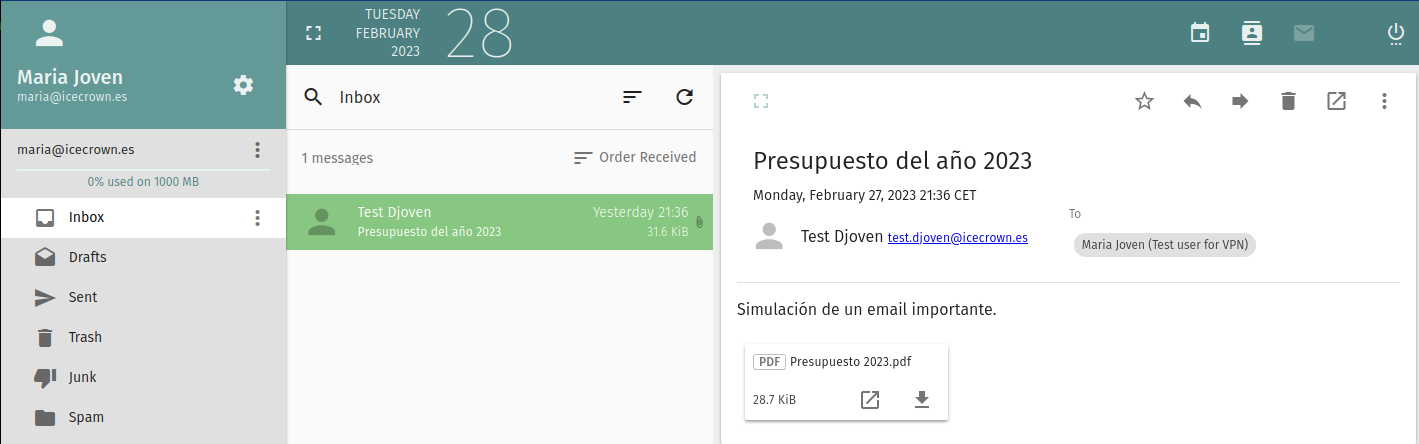
From the user's email account, we verify that we have successfully recovered it along with its attachment.
-
Once the email has been successfully restored, we proceed to unmount the disk and delete the temporary directory created:
-
We detach the EBS volume from the instance, for this, we go to
Actions -> Detach volume: -
Finally, we delete the EBS volume from
Actions -> Delete volume:
System¶
For this section, I will simulate that the system has become completely inoperable because a system administrator has accidentally deleted the zentyal-core package. The general process is as follows:
- We will cause the disaster.
- We will create an EBS volume from the latest available snapshot.
- We will replace the instance volume with the new one.
- We will check that the server is back up and running.
- We will delete the original volume.
To simulate the disaster, I will delete the zentyal-core package.
-
We will log in to the server via SSH and check the status of the Zentyal packages:
The result obtained in my case:
-
We will remove the
zentyal-corepackage to cause instability: -
Finally, we confirm that the modules have been uninstalled, leaving the server inoperable:
The result obtained in my case:
With the disaster properly implemented, we will proceed to restore it using the latest available snapshot.
-
From
EC2 -> Elastic Block Store -> Snapshots -> Create volume from snapshot, we select the latest snapshot and create a volume: -
We configure the volume:
Warning
It must be created in the same availability zone.
-
We verify that the volume has been successfully created and is available:
-
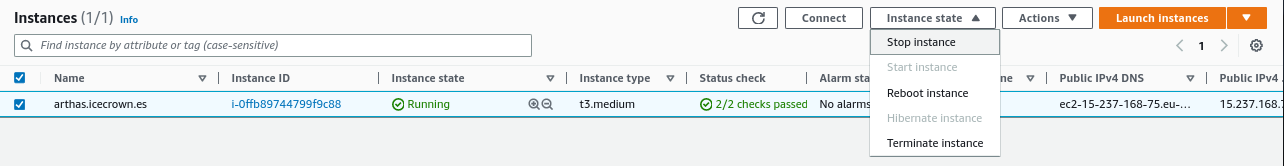
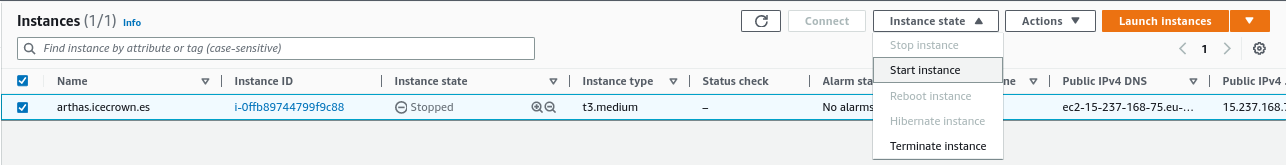
We stop the EC2 instance by going to
EC2 -> Instances -> Instance state: -
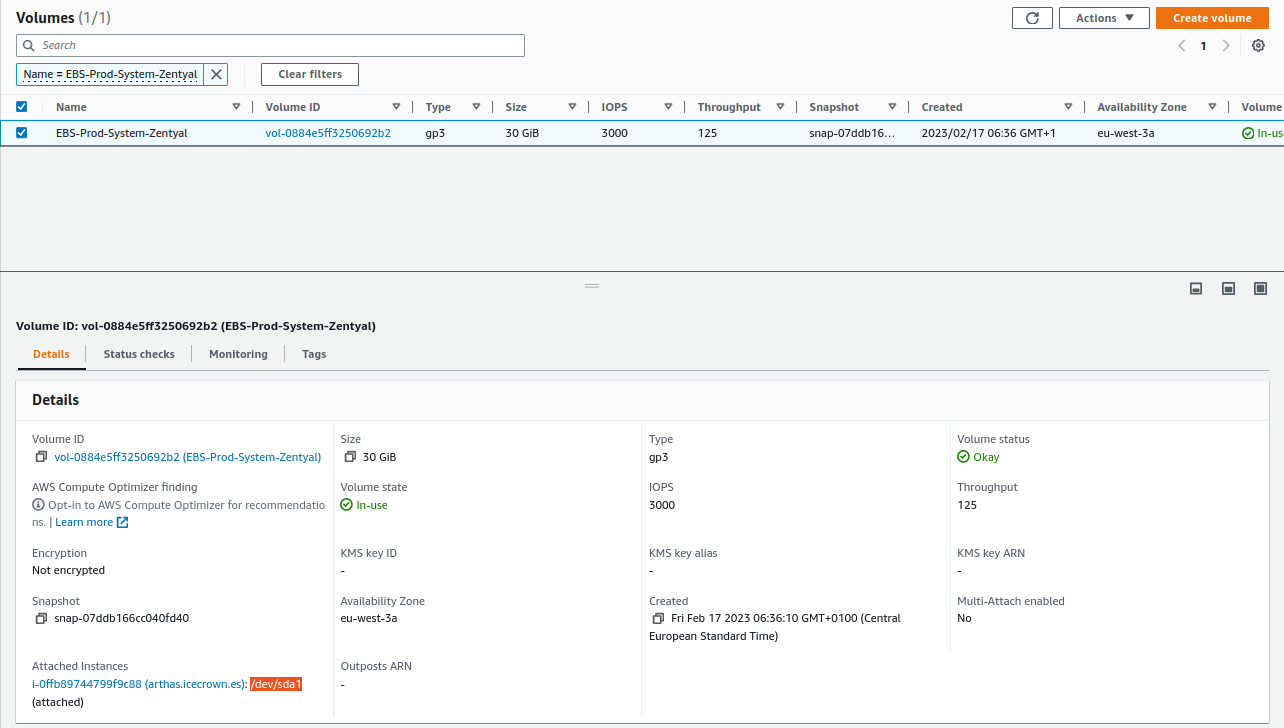
Once stopped, we get the system volume mount point from
EC2 -> Elastic Block Store -> Volumes(option Attached instances): -
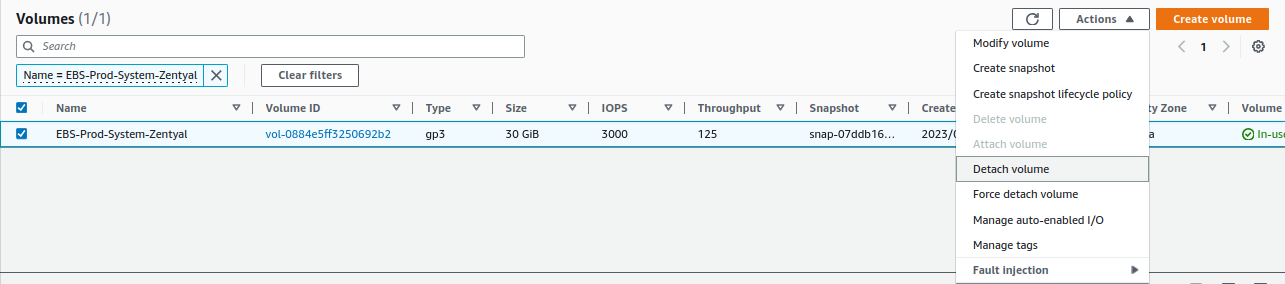
We detach the unstable EBS from the system from
Actions -> Detach volume: -
We attach the new volume created in step 2 from
Actions -> Detach volume:Warning
The mount point (Device name) must be the same as obtained in step 5.
-
We start the instance from
EC2 -> Instances -> Instance state: -
We connect to the instance and check that the packages are properly installed again:
The result obtained in my case:
-
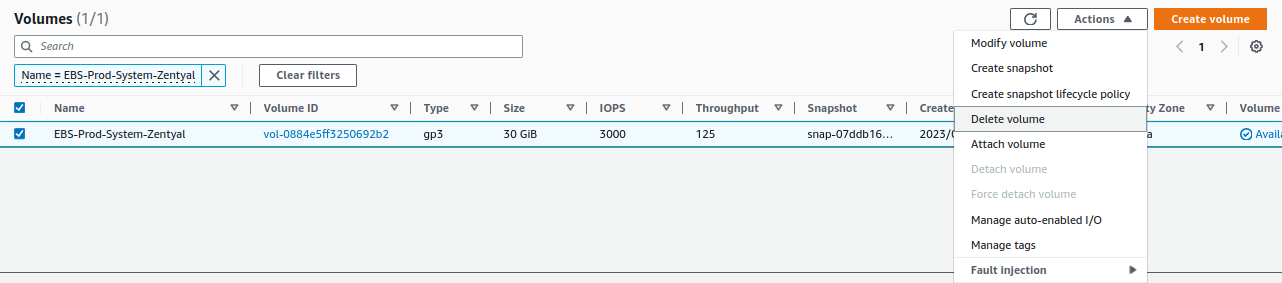
We delete the unstable EBS volume by going to
EC2 -> Elastic Block Store -> Volumes -> Delete volume: -
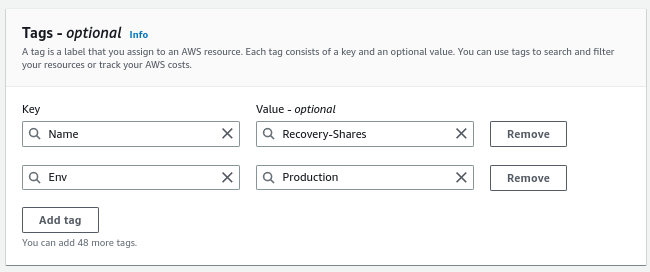
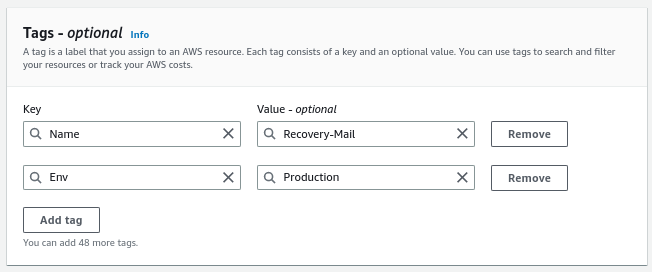
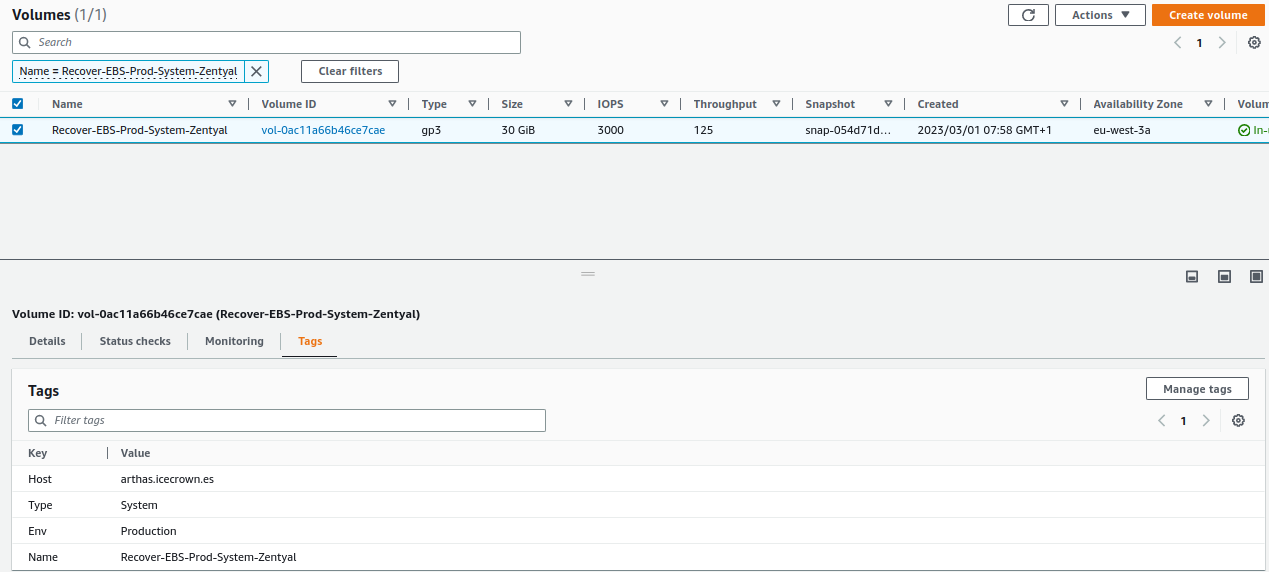
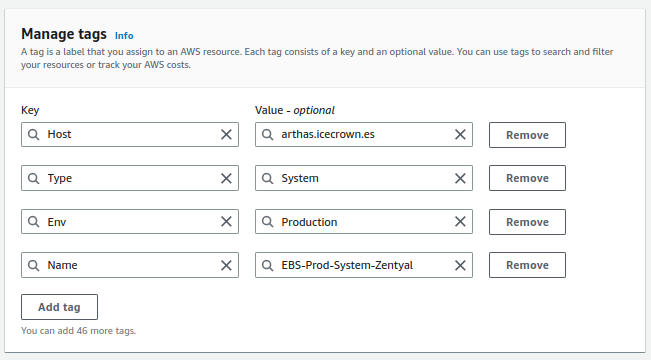
Finally, we modify the
Nametag of the new volume fromTags -> Manage tags:
Created: April 12, 2023